Development of Technologies to Promote Photovoltaic Power Generation as a Primary Power Source
Project overview
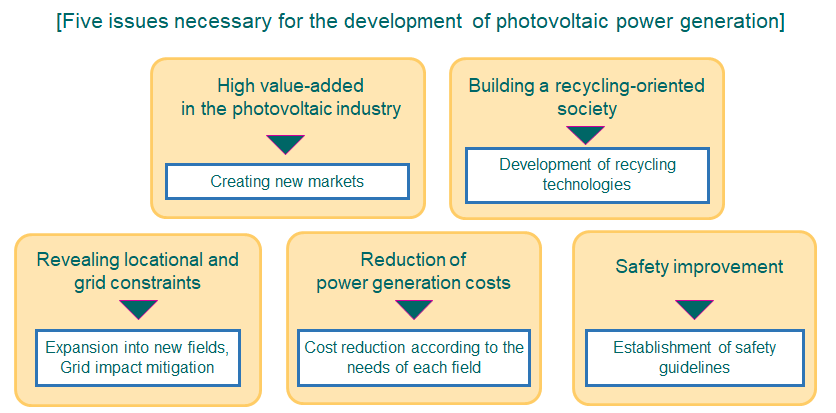
Photovoltaic power generation is the most widespread technology of all the renewable energy, which is expected to become an important domestic low-carbon energy source. In Japan, we are steadily approaching the establishment of a society where photovoltaic power generation is introduced on a mass scale, but various issues have emerged in order to realize such a society.
This project will develop technologies to solve these issues. For example, while the number of suitable sites with favorable conditions for low-cost installation of photovoltaic power generation systems, such as ground-based solar farms and residential roofs, is decreasing, modular system technologies are being developed to enable photovoltaic power generation in new high-demand settings where conventional solar technologies have not been utilized, such as roofs with weight-bearing limits, exterior building walls, and mobility systems.
Furthermore, with a view to resolving issues of making photovoltaic power generation facilities a long-term and stable power source, NEDO will formulate guidelines to contribute to securing safety in areas where photovoltaic power installations are increasingly being installed, such as on sloping lands, water, and farming operations.NEDO will also implement technological development regarding ensuring appropriate maintenance of small-scale commercial photovoltaic power generation facilities as well as assessing and recovering their reliability in an effort to encourage the reinvestment needed to continue the operations of such facilities.
In addition, NEDO will examine low-cost recycling technologies for photovoltaic power generation modules, which are expected to increase rapidly in the future, and methods for overcoming grid constraints, such as output curtailment, on the photovoltaic power generation side. Development of core technologies to support these technologies (such as measurement/assessment methods for new types of batteries and advanced solar radiation forecasting) will also be carried out.
-
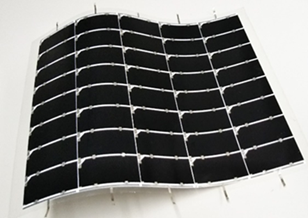 Lightweight and flexible solar cell module with a conversion efficiency of 32.65%
Lightweight and flexible solar cell module with a conversion efficiency of 32.65%
Source: Sharp Corporation -
 Solar panels on building walls
Solar panels on building walls
Source: Kaneka Corporation
Research and Development
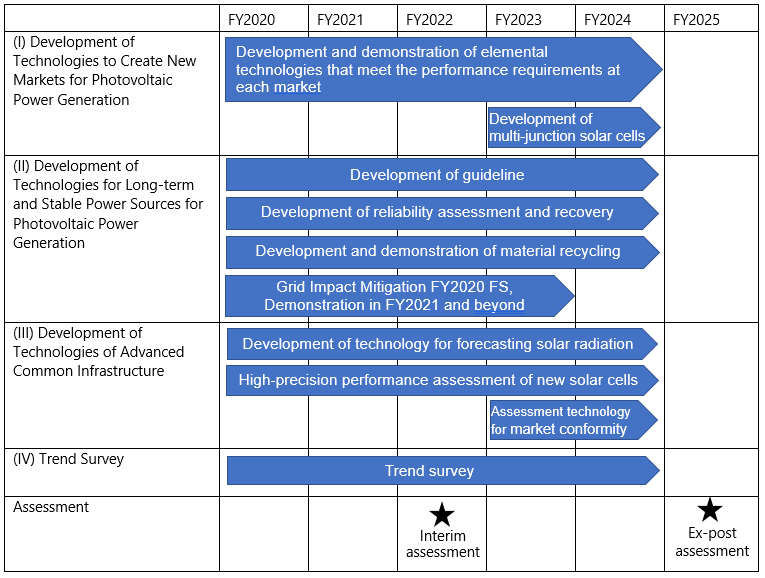
R&D Item [I] Development of PV Power Generation Technologies to Create New Markets
- (i) Development of Film-type Very-lightweight PV Modules
- (ii) Development of Technologies for Wall installed PV Systems
- (iii) Research and Development of PV Power Generation Technologies for Mobility Systems
- (iv) Development of multi-junction solar cell
R&D Item [II] Development of Technologies to Make PV Power Generation a Long-term Stable Power Source
- (i) Development of Technologies to Ensure Safety and Reliability of PV Systems
- (ii) Development of Technologies for PV Module Recycle.
- (iii) Study of Technological Issues to Mitigate the Impacts on the Grid
R&D Item [III] Development of Advanced Common Basic Technologies
R&D Item [IV] Survey of Trends, etc.
Project Manager
SUZUKI Atsuyuki, Duputy Director
Outcome Target
The development of photovoltaic power generation technologies has resulted in the estimation of approximately 320 GW (including approximately 170 GW in the new market*) in terms of domestic cumulative installed capacity as of 2050, and approximately 110 million tons/year (including approximately 630 million tons/year in the new market) in terms of CO2 emissions reduction (compared to grid power sources).
*Total for roofs with weight-bearing limits, exterior building walls, and mobile applications (vehicle-mounted), farming operations, and water.
In addition, the development of long- term and stable technologies for photovoltaic power generation is expected to maintain the amount of installed capacity of 20 GW at power generation facilities, which are mainly small-scale power generation facilities (50 kW or less) expected to be installed as of 2030 (FIT-approved capacity for power generation facilities of 50 kW or less as of December 2018).
Furthermore, it is expected that the development of recycling technologies for photovoltaic power generation facilities will reduce the amount of landfill disposal by approximately 5.1 million tons (estimated for 64 GW of facilities to be installed until 2030).
Output Target
Creation of new markets for photovoltaic power generation will be achieved by developing elemental technologies which fulfill the performance required in places where photovoltaic power generation has not yet been introduced using conventional technologies that contribute to the creation and expansion of each market, as well as by studying the introduction of photovoltaic power generation into the markets based on the estimated amount of power generation. Specifically, NEDO will accelerate the above goals by promoting research and development of basic technologies for mobility systems, roofs with weight-bearing limits, building walls, and other locations where conventional technologies have problems in implementation. At the same time, to ensure operations of long-term and stable projects regarding photovoltaic power generation, which has already been introduced, NEDO will develop technologies that contribute to solving problems that are currently emerging, such as ensuring safety and reliability and overcoming grid constraints in conjunction with developing appropriate business environment, including measures against disposal of power generation facilities. Besides, NEDO will develop common infrastructure technologies that contribute to the above-mentioned fields.
Project Process Control Chart
Basic information
| Technical field |
|
|---|---|
| Project code | P20015 |
| Department in charge |
|
Last Updated : April 21, 2025